Foundation
Protocol upgrades
Stellar protocol upgrades are network-wide changes to consensus and core functionality. Validators must update their software to stay in sync. Upgrades may add new features, improve transaction performance, or strengthen network security.
The Latest
Stability upgrade | protocol 24
Protocol 24 is a stability upgrade necessary to fix a bug in the state archival feature in Stellar Core. Note that the timeline for the upgrade is much more compressed than normal.
Protocol 23
Whisk
CAP-0062
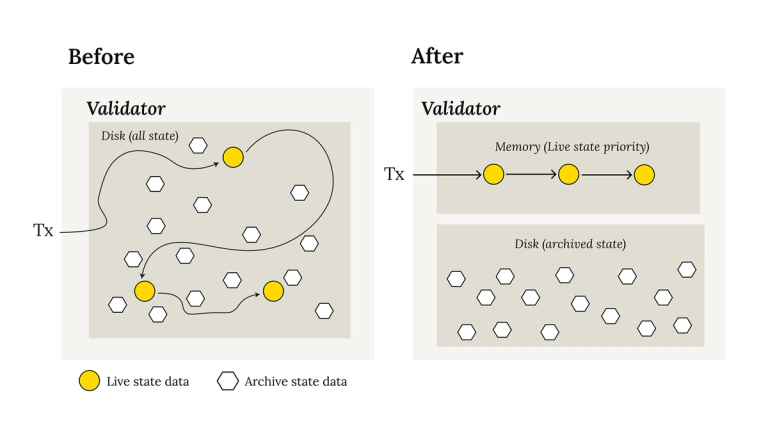
Live state prioritization
This proposal separates archived state and live state into two separate DBs. While these DBs are still both persisted on disk by validators, optimizing live state access is significantly easier. In particular, live state can be entirely cached in memory, removing disk reads from the Soroban transaction execution path, greatly increasing read limits and throughput.
CAP-0063
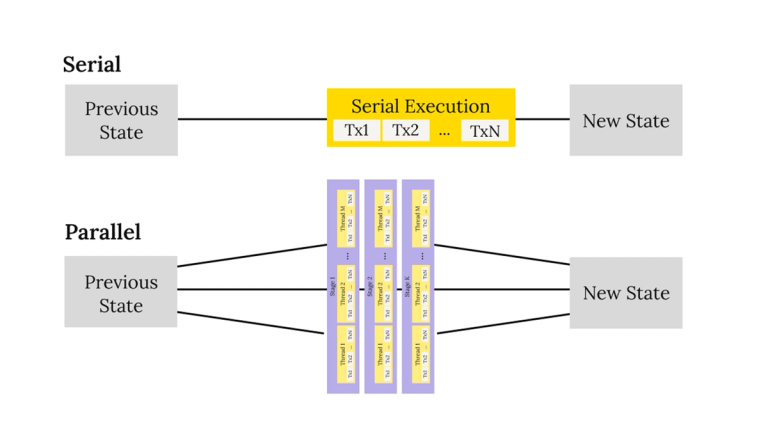
Parallelism-friendly transaction scheduling
Utilizing the idle cores for applying the transactions provides a straightforward way of increasing the number of transactions that may be included into a single ledger block without compromising the time for closing that ledger. This CAP aims to solve this issue and allow for parallelization that has a guaranteed upper bound for the execution time of transaction sets (given at least the minimum specified number of physical threads supported).
Previous upgrades
- Protocol 23 9/3/25 - CAP-0062 (Network evicts persistent entries to archive), CAP-0063 (Parallel smart contract transaction processing), CAP-0065 (Cache parsed WASM modules permanently), CAP-0066 (New Soroban read resource types), CAP-0067 (Standardize Classic and Soroban events), CAP-0068 (Get executable from Soroban address), CAP-0069 (Convert String and Bytes types), CAP-0070 (Dynamic ledger timing configuration settings)
- Protocol 22 12/5/2024 - CAP-0058 (Introduce 'constructor' feature for Soroban smart contracts), CAP-0059 (BLS12-381 host functions).
- Protocol 21 6/18/2024 - CAP-0051 (Support secp256r1 verification), CAP-0053 (Allow extending the Time To Live (TTL)), CAP-0054 (Refining the Soroban cost model used for VM instantiation), CAP-0055 (Lower total costs by linking fewer host functions during VM instantiation), CAP-0056 (Lower total costs by caching parsed Wasm modules)
- Protocol 20 03-19-2024 - CAP-0046-01 (Soroban: Wasm smart contracts for Stellar), CAP-0046-02 (Smart contract structure and creation on Stellar.), CAP-0046-03 (Host functions for Stellar Wasm contracts.), CAP-0046-05 (Smart contract data storage and interaction.), CAP-0046-06 (Allow contracts to interoperate with Stellar assets.), CAP-0046-07 (Smart contract fee mechanism.), CAP-0046-08 (Contract metadata writing for downstream systems.), CAP-0046-09 (Network-wide configuration storage and upgrades.), CAP-0046-10 (Smart contract resource metering framework.), CAP-0046-11 (Smart contract authorization framework.), CAP-0046-12 (Soroban state archival interface.)
- Protocol 19 6-8-2022 - CAP-0021 (Generalized transaction conditions and timelocks.), CAP-0040 (Shared transaction signing for contracts.)
- Protocol 18 11-3-2021 - CAP-0038 (Automated market marker liquidity.)
- Protocol 17 6-1-2021 - CAP-0035 (Asset clawback for regulatroy compliance.)
- Protocol 16 4-10-2021 - CAP- 0029 (Issuer trustline authorization semantics.)
- Protocol 15 11-23-2020 - CAP-0023 (Separate payment sending and receiving.), CAP-0033 (Cross-account reserve payments), CAP-0034 (Nomination protocol close time selection)
- Protocol 13 6-18-2020 - CAP-0015 (Fee-bump transactions for arbitrary accounts), CAP-0018 (Partial trustline authorization for issuers.), CAP-0019 (Extensible transaction envelope union.), CAP-0027 (Multiplexed accounts with memo IDs.), CAP-0028 (Pre-auth signer removal on application.), CAP-0030 (Remove unnecessary asset issuer errors.)
- Protocol 12 10-10-2019 - CAP-0024 (PathPayment with fixed send amount.), CAP-0025 (Bucket list simplification removing shadows.), CAP-0026 (Disables the inflation mechanism.)
- Protocol 11 6-10-2019 - CAP-0005 (Network throttling and fee rationalization), CAP-0006 (ManageBuyOffer operation for buying asset.), CAP-0020 (Bucket entry type extensions.)
- Protocol 10 2-8-2018 - CAP-0001 (Bump sequence operation.), CAP-0002 (Consistent signature verification for contracts), CAP-0003 (Asset-backed offers execution guarantee.), CAP-0004 (Offer crossing algorithm improvements.)